OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
更新済 Kaufman's Adaptive Moving Average (KAMA) - Multi timeframe
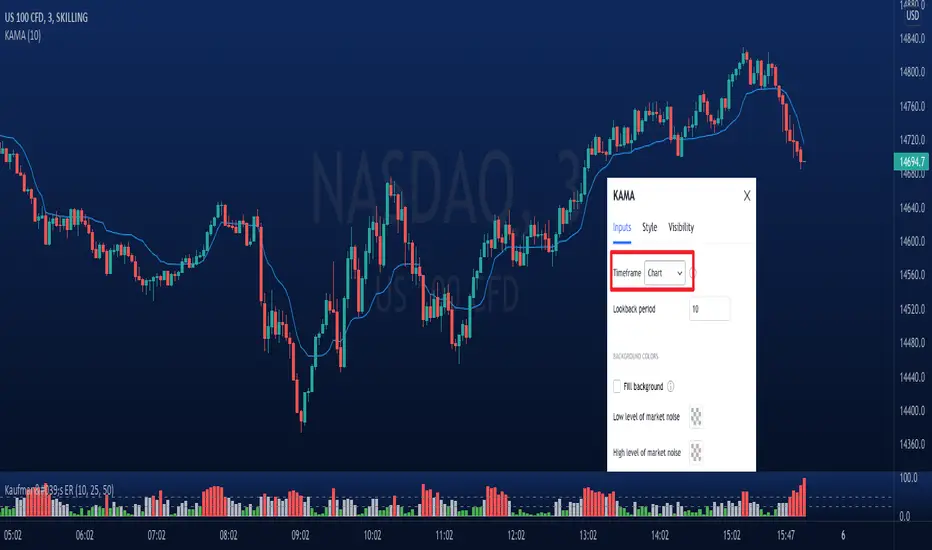
Kaufman's Adaptive Moving Average (KAMA)
KAMA was developed by Perry Kaufman to give better directions of short term market trends.
Idea is similar to an EMA, but it makes adjustments to the smoothing factor by taking Market Noise into consideration. Levels of noise in KAMA is modelled using Kaufman's Efficiency Ratio.
The problem with traditional of moving averages (ie. SMA/EMA) is that they are very sensitive to sudden price movements.
Applications:
- Less prone to false signals compared to other types of moving averages. When price suddenly surges or tanks, KAMA will lag behind telling us that the move is rather abnormal.
- On the other hand, when volatility of price movements is low, KAMA will be close to the ranging candles with a slope approximate to zero. KAMA can be used for filtering out choppy markets.
Other features:
- Multi-timeframe.
- Can visualize levels of market noise with background color mode turned on.
KAMA was developed by Perry Kaufman to give better directions of short term market trends.
Idea is similar to an EMA, but it makes adjustments to the smoothing factor by taking Market Noise into consideration. Levels of noise in KAMA is modelled using Kaufman's Efficiency Ratio.
The problem with traditional of moving averages (ie. SMA/EMA) is that they are very sensitive to sudden price movements.
Applications:
- Less prone to false signals compared to other types of moving averages. When price suddenly surges or tanks, KAMA will lag behind telling us that the move is rather abnormal.
- On the other hand, when volatility of price movements is low, KAMA will be close to the ranging candles with a slope approximate to zero. KAMA can be used for filtering out choppy markets.
Other features:
- Multi-timeframe.
- Can visualize levels of market noise with background color mode turned on.
リリースノート
New feature: Coded candles to identify price crossing with MA.リリースノート
Amended line 43, calling of nz(src=kama, replacement=close). Previously, param. replacement==0リリースノート
Features:- Added: Option to show smooth KAMA (least of squares over same KAMA period).
- Added: Low/high thresholds for background colors linked to noise (if turned on)
- Removed: bar colors during crosses
オープンソーススクリプト
TradingViewの精神に則り、このスクリプトの作者はコードをオープンソースとして公開してくれました。トレーダーが内容を確認・検証できるようにという配慮です。作者に拍手を送りましょう!無料で利用できますが、コードの再公開はハウスルールに従う必要があります。
Read Faster & Learn Anything with Coral AI! getcoralai.com//?ref=dojiemoji
免責事項
この情報および投稿は、TradingViewが提供または推奨する金融、投資、トレード、その他のアドバイスや推奨を意図するものではなく、それらを構成するものでもありません。詳細は利用規約をご覧ください。
オープンソーススクリプト
TradingViewの精神に則り、このスクリプトの作者はコードをオープンソースとして公開してくれました。トレーダーが内容を確認・検証できるようにという配慮です。作者に拍手を送りましょう!無料で利用できますが、コードの再公開はハウスルールに従う必要があります。
Read Faster & Learn Anything with Coral AI! getcoralai.com//?ref=dojiemoji
免責事項
この情報および投稿は、TradingViewが提供または推奨する金融、投資、トレード、その他のアドバイスや推奨を意図するものではなく、それらを構成するものでもありません。詳細は利用規約をご覧ください。