OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Forex Pair Yield Momentum
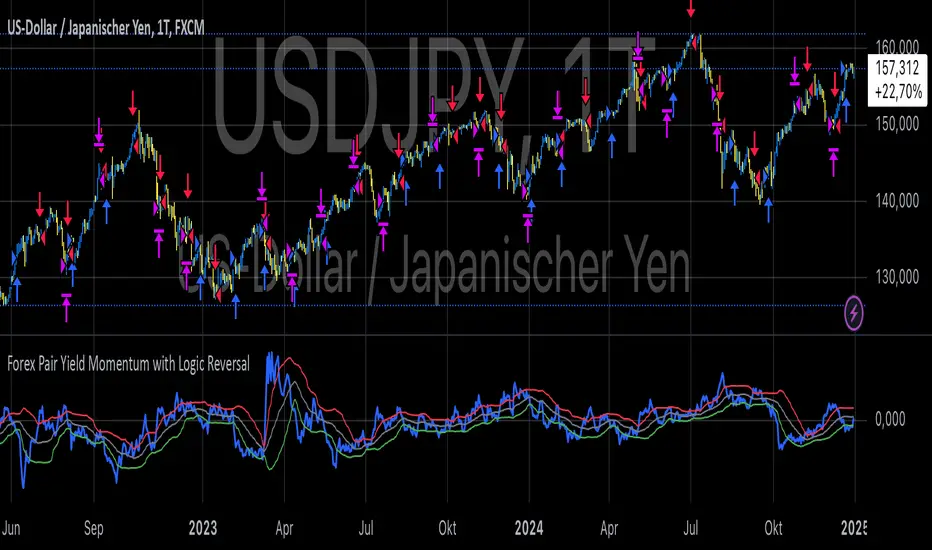
This Pine Script strategy leverages yield differentials between the 2-year government bond yields of two countries to trade Forex pairs. Yield spreads are widely regarded as a fundamental driver of currency movements, as highlighted by international finance theories like the Interest Rate Parity (IRP), which suggests that currencies with higher yields tend to appreciate due to increased capital flows:
1. Dynamic Yield Spread Calculation:
• The strategy dynamically calculates the yield spread (yield_a - yield_b) for the chosen Forex pair.
• Example: For GBP/USD, the spread equals US 2Y Yield - UK 2Y Yield.
2. Momentum Analysis via Bollinger Bands:
• Yield momentum is computed as the difference between the current spread and its moving
Bollinger Bands are applied to identify extreme deviations:
• Long Entry: When momentum crosses below the lower band.
• Short Entry: When momentum crosses above the upper band.
3. Reversal Logic:
• An optional checkbox reverses the trading logic, allowing long trades at the upper band and short trades at the lower band, accommodating different market conditions.
4. Trade Management:
• Positions are held for a predefined number of bars (hold_periods), and each trade uses a fixed contract size of 100 with a starting capital of $20,000.
Theoretical Basis:
1. Yield Differentials and Currency Movements:
• Empirical studies, such as Clarida et al. (2009), confirm that interest rate differentials significantly impact exchange rate dynamics, especially in carry trade strategies .
• Higher-yields tend to appreciate against lower-yielding currencies due to speculative flows and demand for higher returns.
2. Bollinger Bands for Momentum:
• Bollinger Bands effectively capture deviations in yield momentum, identifying opportunities where price returns to equilibrium (mean reversion) or extends in trend-following scenarios (momentum breakout).
• As Bollinger (2001) emphasized, this tool adapts to market volatility by dynamically adjusting thresholds .
References:
1. Dornbusch, R. (1976). Expectations and Exchange Rate Dynamics. Journal of Political Economy.
2. Obstfeld, M., & Rogoff, K. (1996). Foundations of International Macroeconomics.
3. Clarida, R., Davis, J., & Pedersen, N. (2009). Currency Carry Trade Regimes. NBER.
4. Bollinger, J. (2001). Bollinger on Bollinger Bands.
5. Mendelsohn, L. B. (2006). Forex Trading Using Intermarket Analysis.
1. Dynamic Yield Spread Calculation:
• The strategy dynamically calculates the yield spread (yield_a - yield_b) for the chosen Forex pair.
• Example: For GBP/USD, the spread equals US 2Y Yield - UK 2Y Yield.
2. Momentum Analysis via Bollinger Bands:
• Yield momentum is computed as the difference between the current spread and its moving
Bollinger Bands are applied to identify extreme deviations:
• Long Entry: When momentum crosses below the lower band.
• Short Entry: When momentum crosses above the upper band.
3. Reversal Logic:
• An optional checkbox reverses the trading logic, allowing long trades at the upper band and short trades at the lower band, accommodating different market conditions.
4. Trade Management:
• Positions are held for a predefined number of bars (hold_periods), and each trade uses a fixed contract size of 100 with a starting capital of $20,000.
Theoretical Basis:
1. Yield Differentials and Currency Movements:
• Empirical studies, such as Clarida et al. (2009), confirm that interest rate differentials significantly impact exchange rate dynamics, especially in carry trade strategies .
• Higher-yields tend to appreciate against lower-yielding currencies due to speculative flows and demand for higher returns.
2. Bollinger Bands for Momentum:
• Bollinger Bands effectively capture deviations in yield momentum, identifying opportunities where price returns to equilibrium (mean reversion) or extends in trend-following scenarios (momentum breakout).
• As Bollinger (2001) emphasized, this tool adapts to market volatility by dynamically adjusting thresholds .
References:
1. Dornbusch, R. (1976). Expectations and Exchange Rate Dynamics. Journal of Political Economy.
2. Obstfeld, M., & Rogoff, K. (1996). Foundations of International Macroeconomics.
3. Clarida, R., Davis, J., & Pedersen, N. (2009). Currency Carry Trade Regimes. NBER.
4. Bollinger, J. (2001). Bollinger on Bollinger Bands.
5. Mendelsohn, L. B. (2006). Forex Trading Using Intermarket Analysis.
オープンソーススクリプト
TradingViewの精神に則り、このスクリプトの作者はコードをオープンソースとして公開してくれました。トレーダーが内容を確認・検証できるようにという配慮です。作者に拍手を送りましょう!無料で利用できますが、コードの再公開はハウスルールに従う必要があります。
Where others speculate, we systematize.
edgetools.org
edgetools.org
免責事項
この情報および投稿は、TradingViewが提供または推奨する金融、投資、トレード、その他のアドバイスや推奨を意図するものではなく、それらを構成するものでもありません。詳細は利用規約をご覧ください。
オープンソーススクリプト
TradingViewの精神に則り、このスクリプトの作者はコードをオープンソースとして公開してくれました。トレーダーが内容を確認・検証できるようにという配慮です。作者に拍手を送りましょう!無料で利用できますが、コードの再公開はハウスルールに従う必要があります。
Where others speculate, we systematize.
edgetools.org
edgetools.org
免責事項
この情報および投稿は、TradingViewが提供または推奨する金融、投資、トレード、その他のアドバイスや推奨を意図するものではなく、それらを構成するものでもありません。詳細は利用規約をご覧ください。