OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
MACD Normalized [ChartPrime]
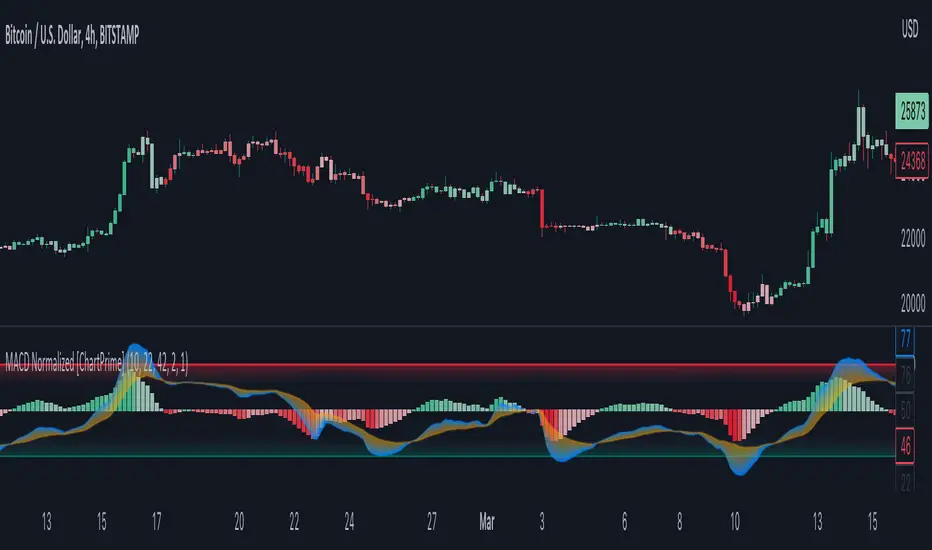
Overview of MACD Normalized Indicator
The MACD Normalized indicator, serves as an asset for traders seeking to harness the power of the moving average convergence divergence (MACD) combined with the advantages of the stochastic oscillator. This novel indicator introduces a normalized MACD, offering a potentially enhanced flexibility and adaptability to numerous market conditions and trading techniques.
This indicator stands out by normalizing the MACD to its average high and average low, also factoring in the deviation of the high-low position from the mean. This approach incorporates the high and low in the calculations, providing the benefits of stochastic without its common drawbacks, such as clipping problems. As a result, the indicator becomes exceptionally versatile and suitable for various trading strategies, including both faster and slower settings.
The MACD Normalized Indicator boasts a variety of options and settings. The features include:
Use Cases for the MACD Normalized Indicator
In addition to analyzing market trends and identifying potential trading opportunities, ChartPrime's MACD Normalized Indicator offers a range of applications for traders. These use cases encompass distinct trading scenarios and strategies:
Overbought and Oversold Regions
One of the key applications of the MACD Normalized Indicator is identifying overbought and oversold regions. Overbought refers to a situation where an asset's price has risen significantly and is expected to face a downturn, while oversold indicates a price drop that may subsequently lead to a reversal.
By adjusting the indicator's parameters, such as the upper and inner deviation levels, traders can set precise boundaries to determine overbought and oversold areas. When the MACD moves into the upper region, it may signal that the asset is overbought and due for a price correction. Conversely, if the MACD enters the lower region, it possibly indicates an oversold condition with the potential for a price rebound.

Signal Line Crossovers
The MACD Normalized Indicator displays two lines: the fast line and the slow line (inner band). A common trading strategy involves observing the intersection of these two lines, known as a crossover. When the fast line crosses above the slow line, it may signify a bullish trend or a potential buying opportunity. Conversely, a crossover with the fast line moving below the slow line typically indicates a bearish trend or a selling opportunity.
Divergence and Convergence
Divergence occurs when the price movement of an asset does not align with the corresponding MACD values. If the price establishes a new high while the MACD fails to do the same, a bearish divergence emerges, suggesting a potential downtrend. Similarly, a bullish divergence takes place when the price forms a new low but the MACD does not follow suit, hinting at an upcoming uptrend.
Convergence, on the other hand, is represented by the MACD lines moving closer together. This movement signifies a potential change in the trend, providing traders with a timely opportunity to enter or exit the market.
The MACD Normalized indicator, serves as an asset for traders seeking to harness the power of the moving average convergence divergence (MACD) combined with the advantages of the stochastic oscillator. This novel indicator introduces a normalized MACD, offering a potentially enhanced flexibility and adaptability to numerous market conditions and trading techniques.
This indicator stands out by normalizing the MACD to its average high and average low, also factoring in the deviation of the high-low position from the mean. This approach incorporates the high and low in the calculations, providing the benefits of stochastic without its common drawbacks, such as clipping problems. As a result, the indicator becomes exceptionally versatile and suitable for various trading strategies, including both faster and slower settings.
The MACD Normalized Indicator boasts a variety of options and settings. The features include:
- Enable Ribbon: Toggle the display of the ribbon accompanying the MACD Normalized, as desired.
- Fast Length: Determine the movement speed of the fast line to receive advance notice of potential market opportunities.
- Slow Length: Control the movement pace of the slow line for smoother signals and a comprehensive outlook on market trends.
- Average Length: Specify the length used to calculate the high and low averages, providing greater control over the indicator's granularity.
- Upper Deviation: Establish the extent to which the high and low values deviate from the mean, ensuring adaptability to diverse market situations.
- Inner Band (Middle Deviation): Adjust the balance between the high and low deviations to create an inner band signal, giving traders a secondary level of market analysis and decision-making support.
- Enable Candle Color: Enable the coloring of candles based on the MACD Normalized value for effortless visualization of trading potential.
Use Cases for the MACD Normalized Indicator
In addition to analyzing market trends and identifying potential trading opportunities, ChartPrime's MACD Normalized Indicator offers a range of applications for traders. These use cases encompass distinct trading scenarios and strategies:
Overbought and Oversold Regions
One of the key applications of the MACD Normalized Indicator is identifying overbought and oversold regions. Overbought refers to a situation where an asset's price has risen significantly and is expected to face a downturn, while oversold indicates a price drop that may subsequently lead to a reversal.
By adjusting the indicator's parameters, such as the upper and inner deviation levels, traders can set precise boundaries to determine overbought and oversold areas. When the MACD moves into the upper region, it may signal that the asset is overbought and due for a price correction. Conversely, if the MACD enters the lower region, it possibly indicates an oversold condition with the potential for a price rebound.
Signal Line Crossovers
The MACD Normalized Indicator displays two lines: the fast line and the slow line (inner band). A common trading strategy involves observing the intersection of these two lines, known as a crossover. When the fast line crosses above the slow line, it may signify a bullish trend or a potential buying opportunity. Conversely, a crossover with the fast line moving below the slow line typically indicates a bearish trend or a selling opportunity.
Divergence and Convergence
Divergence occurs when the price movement of an asset does not align with the corresponding MACD values. If the price establishes a new high while the MACD fails to do the same, a bearish divergence emerges, suggesting a potential downtrend. Similarly, a bullish divergence takes place when the price forms a new low but the MACD does not follow suit, hinting at an upcoming uptrend.
Convergence, on the other hand, is represented by the MACD lines moving closer together. This movement signifies a potential change in the trend, providing traders with a timely opportunity to enter or exit the market.
オープンソーススクリプト
TradingViewの精神に則り、このスクリプトの作者はコードをオープンソースとして公開してくれました。トレーダーが内容を確認・検証できるようにという配慮です。作者に拍手を送りましょう!無料で利用できますが、コードの再公開はハウスルールに従う必要があります。
免責事項
この情報および投稿は、TradingViewが提供または推奨する金融、投資、トレード、その他のアドバイスや推奨を意図するものではなく、それらを構成するものでもありません。詳細は利用規約をご覧ください。
オープンソーススクリプト
TradingViewの精神に則り、このスクリプトの作者はコードをオープンソースとして公開してくれました。トレーダーが内容を確認・検証できるようにという配慮です。作者に拍手を送りましょう!無料で利用できますが、コードの再公開はハウスルールに従う必要があります。
免責事項
この情報および投稿は、TradingViewが提供または推奨する金融、投資、トレード、その他のアドバイスや推奨を意図するものではなく、それらを構成するものでもありません。詳細は利用規約をご覧ください。